Need-to-Know Web Design Terms
Table of Contents
-
-
-
Above the fold
Accordion
Alt text
Announcement bar
Anchor link
Backlink
Below the fold
Bounce Rate
Broken link / 404
Browser
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CTA (Call to Action)
CRO (Conversion Rate Optimisation)
Cookies
Domain
E-commerce
Favicon
GDPR
Hosting
HTML
Keywords
Landing Page
Lazy Load
Lightbox
Loading Speed (Page Loading Speed)
Navigation
Metadescription
Meta Pixel (Facebook Pixel)
Parallax scroll
Platform
Responsive
Skimmability
Sticky Nav / Header
SEO
Subdomain
Theme / Template
User Journey
User Experience
This post may contain affiliate links which mean I may receive a commission for purchases made through these links (at no cost to you, of course!)
Leather-hard. Backward loop. Burnishing. Every craft has their own unique language that helps you to communicate with your peers. Web design is no different, we have our own terminology!
These terms help you to explain what you’re trying to achieve in a way others can follow. You take for granted how much you know. That is until you try out a new creative avenue and realise there’s a whole other vocabulary you need to learn!
Well, we web designers have a large vocabulary of words too and it helps to be aware of what they each mean so you can make the best out of your relationship with your web designer.
Here's how to speak the lingo so you can get your point across with your web designer, and sound like a pro!
Design Terms
Branding
Branding is the art of giving meaning to a specific organisation, company, products or services by creating and shaping a brand in the consumer’s mind. It reinforces and complements the existing reputation of a brand. Your brand identity includes your logo, typography, colour palette, messaging, brand values and strategy.
Colour Palette
A set of colours that represents your brand personality. These colours will be used in your logo, on your website and across all marketing collateral.
Some well-known colour palettes
Information Hierarchy
A visual design principle to show the importance and priority of specific pieces of information by varying size and colour. This helps guide the user through the information, helping to improve the user experience.
Margin
The space around an element to keep a gap between itself and other elements. A margin can apply to all four sides of the element or specific to each side individually.
Padding
The space inside an element to avoid inner elements to touch the edge. It can also apply to all four sides of the element or specific to each side individually.
White Space (Negative Space)
The empty space around content and elements on a web page. White space is used to balance a page’s design, giving breathing room for the user to take in the information and improve the visual user experience.
Typography
Custom Font
A font that is not a default of the website platform. It is usually a new and unique design that may have been designed for use in print but will have a web version. It requires you to import it into the website and may slow down the site.
You can find beautiful custom fonts at Creative Market.
Font Family
A set of fonts that have a common design but may vary styles, such as weight, slant and letter width. For example, Roboto is a font family, but within the family, there are 12 styles. Here is a snippet of 4 of them.
Hierarchy
Similar to information hierarchy. It is the importance and priority given to text so that it is clear which should be read first to last. This is done by grouping styles such as Heading 1, Heading 2, Heading 3, Paragraph 1, Paragraph 2, Small Copy. Design may change between these groups depending on font family, colour and most importantly size.
Legibility
The ease at which a reader can distinguish the letters and symbols in a word. This can depend on font size, line height and font weight.
Letter Spacing
The space between each letters in a word to change the visual density of a line or block of text. If the letter spacing is too little, the letters will touch each other and affect readability. When the letter spacing is too wide, letters can no longer feel like part of a word.
Line Height / Leading
The horizontal space between lines in a paragraph. If the spacing is too little, the lower parts of one line may touch the top part of another.
Lorem Ipsum
This is a standardised placeholder text which designers use to show text looking as realistic as possible without having the actual text.
Readability
The ease at which a reader can understand the written text overall. This can depend on the font choice, spacing and colours used as well as the context of the words.
Sans-Serif Font
A sans serif font is missing the serif (see below). This style of font is usually attributed to being more modern and minimal therefore making it preferred for websites.
Serif Font
The serif is a small line or stroke attached to the end of a letter stroke. This style of font is usually attributed to being a more traditional style.
An example of a Serif and Sans-Serif Font.
Web Fonts
A font that has been especially created for websites and often comes up as a default on the website platform. Web fonts will load faster on a site.
You can find beautiful web fonts at Google Fonts or Adobe Fonts (previously Typekit). Please note, Adobe Fonts required a paid subscription.
Weight
The thickness or thinness of a font ranging from 100 (extra light) to 900 (extra bold). This is instead of simply “bold” which doesn’t give much flexibility for design.
Website Terms:
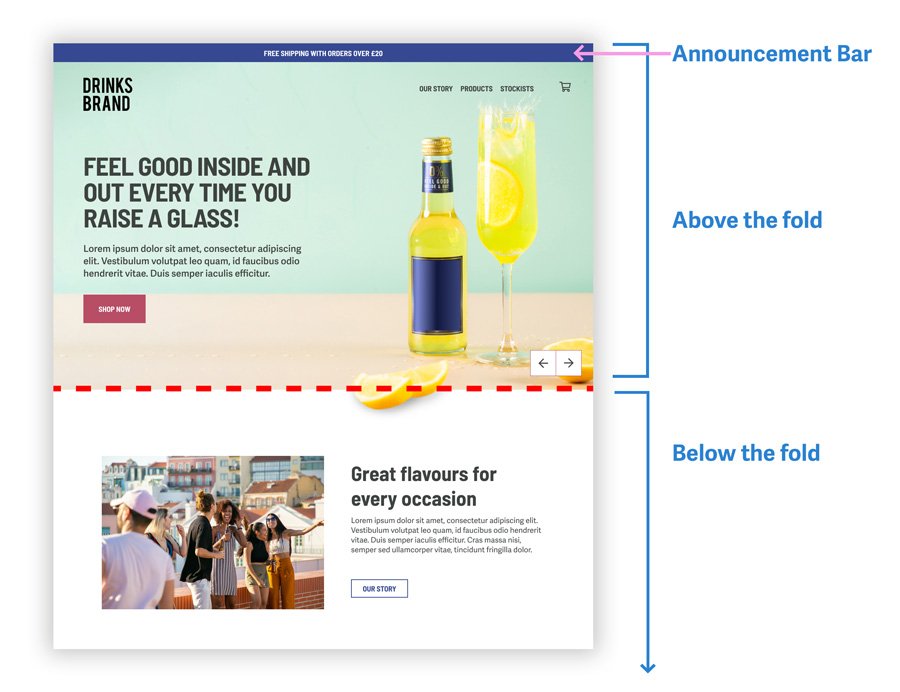
Above the fold
The upper part of the webpage that displays before needing to scroll. This is prime real estate for content and call-to-actions and so the content needs to be engaging and grab the user’s attention right away.
Accordion
A way of displaying information as a list stacked on top of each other. When clicked, the information opens up to show more content. This is especially useful when you don’t want to overwhelm your readers with too much information and make it easy for them to find what they are looking for. It could be used for FAQs, process steps, services. Example below:
-
who knows this reference?
-
oh hey Neil Buchanan
-
cue the music…
Alt Text
Also Alternative Text. This is a word or phrase that is hidden in your image’s code that appears in place of an image if the image fails to load. This is used for SEO (bringing in keywords) and helping with accessibility.
Announcement bar
A banner message that appears in a bar across the top of your site, visible on your mobile and desktop sites. This is a great way to bring attention to an offer.
Anchor Link
A way to jump to a specific part of a webpage, rather than to the top. This is done by adding a small code at the specific section of the page that you want to jump to and adding an anchor id. It saves you having loads of shallow pages and lets you include more content on less pages while still giving the user the change to navigate their way around the site.
Backlink
A link back to your website from another website. This is great for SEO!
Below the fold
This is the webpage content that is not initially visible when visiting a site. The user will have to scroll down to see this information (see above the fold).
Bounce Rate
The percentage of visitors who leave your page after visiting one page. You ideally want this to be as low as possible as you want visitors to be on your site for as long as is needed to digest all of your information.
Broken link / 404
A link to a webpage that is no longer there or has an error. It could also be a typo in the link url. Its a great chance to show your brand’s tone of voice. Here’s an example of mine.
Browser
Also known as a web browser. This is the app/program you use to view websites on such as Safari, Chrome, Mozilla, Firefox and Opera. Each browser differs in how they’re built and what they offer so websites may appear slightly different.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
A code language used to style elements of code. This can be used to adjust the colour, fonts, size, rotation etc. I love using this to make my designs exactly how I want!
CTA (Call to Action)
A design tool used to prompt an immediate response from the visitor, ie to click through to another page, email or download a file. It could be in the form of a button or text.
CRO (Conversion Rate Optimisation)
The process of increasing the percentage of website visitors to take a desired action. This can be done through using clear call-to-actions and improving the user journey so the customer is lead through the relevant steps easily.
A piece of data from a website that is stored within a web browser that can be used at a later date.
Domain
This is the name of a website in the form or a URL. It is the website address you type in at the top of a browser to visit a website. It can be a powerful SEO tool for customers to find you.
Want to find out how to choose the right domain name for your business?
E-commerce
Short for Electric Commerce, is a website that allows people to buy and sell products, services and/or digital products over the internet rather than in person.
Favicon
The tiny image at the top of your web browser that acts as an extension of your brand, letting your visitors know which website they are viewing (especially if they have loads of tabs open). It’s usually a key part of your logo that is easily identifiable. See mine below:
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation is a EU law regulation on data protection and privacy. It helps website visitors to know their information is protected and will not be sold off to third parties. It is important that if you are doing business in the EU and EEA (European Economic Area) or may have visitors from this area, that your website is GDPR compliant.
Hosting
A service that hosting providers offer to store your website on their servers. Some web building platforms include this in their plans (like Squarespace, Shopify and Wix) whereas some platforms require you to purchase this separately (Wordpress).
HTML
Short for HyperText Markup Language, is a coding language displaying in a web browser. It works hand in hand with CSS and Javascript to create the website you see in front of you.
Keywords
Words or phrases in the content of your webpages that match the word or phrases your customers are entering into search engines (like Google or Bing). They allow you to build an SEO strategy around targeting specific audiences through the words or phrases they will most likely search fro.
Landing Page
A standalone page that a website visitor “lands” on after clicking through from an ad, social media post or email which has a very specific goal in mind.
Lazy Load
This is when content on the webpage is not all downloaded at once but is slowly loaded in the background as you scroll down the site. This allows the site to load faster.
Lightbox
A popup or window overlay that appears over a webpage blocking the rest of the content behind it, giving the visitors full attention to the content in the popup.
Lightbox
Loading Speed (Page Loading Speed)
The time it takes a webpage to fully load/be displayed on a website. We want this to be as fast as possible and can do this by optimising images, reducing CSS/scripts and using the best hosting server on offer so that our audience don’t get tired of waiting and leave the site.
This is the list of pages/links at the top of your website that enables your users to visit other pages. It is important to make sure this area isn’t too overcrowded and to group pages where possible.
Meta Description
One of the web page’s on-page SEO data. It is the description that shows what the page is about and shows up along with the SEO title in search engines (Google, Bing) as well as when your page is shared on social media. It’s important this include keywords to attract your audience.
Meta Pixel (Facebook Pixel)
A piece of code that sits in the header of your website that allows you to measure the effectiveness of your advertising/marketing. It is used to understand the actions that your customers carry out on your site such as page views, product views, adding to cart, starting checkout and purchases. Here’s how to set up and install your Facebook Pixel.
Parallax Scroll
A web design technique where an image/or background image of a specific section moves at a different pace than the foreground. It results in a 3D effect and can be a clever way to bring a dynamic feel to your website.
Platform
This is the software that your website is built in. It can either be a standalone part of your website that works hand-in-hand with your domain and hosting, or it could be part of an all-in-one solution like Squarespace, Shopify or Wix.
Responsive
Usually used as “device responsive” to explain how well a website can adapt to varying device sizes. All websites should be responsive to mobile devices as standard practice. The design will differ and elements of a site will become stacked rather than side-by-side to adapt to the narrower page width.
Skimmability
The ease of being able to skim/scan through a web page to find the information you are interested in as well as the most important information. This is done by making use of clear headings, highlighting pull quotes, using a table of contents and separating out content as sidebars.
A fixed navigation menu on a webpage that stays in the same position as you scroll down the site. This helps the user to easily access other pages at any time instead of having to scroll all the way back to the top of the page.
SEO
Short for ‘Search Engine Optimisation’ is the process of improving your site to increase visibility when people search for key terms, ideally getting your site to the top spot of the search engine results. This can be done by improving on-page SEO, backlinks, image alt-tags and using the best keywords for your brand throughout your site.
Subdomain
This is a sub-section of your website/domain created to organise your pages. It may appear as clients.yourdomain.com rather than yourdomain.com/clients
Theme / Template
Used interchangeably web development depending on the platform. It is a predesigned resource that sets out the structure for the overall layout & features of a website. These are used by web designers to start as a base to work on.
User Journey
A path a user may take to reach a goal when using a website, ideally keeping the path as short as possible to ensure higher conversion rates.
User Experience (UX)
How a user interacts with and experiences a website including a person’s perception of utility, easy of use and efficiency. It’s important to make sure the UX is as positive as possible to keep the user happy and on the site for longer.